The Anatomy and Morphology of hemp
The Hemp (or cannabis) plant, is famous globally because of its iconic shape of leafs. In this post I'm going to talk more in dept about some characteristics of the hemp plant that are also recognisable from the outside, but may not be known for people who's knowledge does not go beyond the point of recognising the shape of the leaf.
Monocot or dipot?
The distinction between monocot and dicot plant is pretty easy to determine from outside. First of all, you can take a look at the flowers. If the flower is in parts of threes or a multiplied version of this, it is a monocot plant. If the flower is made up in parts of fours and fives of a multiplied version of this, the plan is a dicot.

(Source: http://www.ext.colostate.edu/mg/gardennotes/135.html)
Another way to indentify if a plant is a monocot or dicot, is to look at the leafs. Monocot leafs have the veins parallel to each other, while dicot leafs are branches and netlike. This is easy to see in the next picture, when comparing grass to a dicot leaf.

(Source: http://www.majordifferences.com/2014/04/difference-between-monocot-and-dicot.html#.Wb55c8hJbIU)
Is Hemp a monocot or dicot?
The leafs of the Hemp plant indicate that it is a dicot. But what other features can indicate whether hemp is a monocot or dicot? and what are the differences?
Cotyledons
This are the primary leafs in the seed of which the hemp plants has two (instead of one for monocots). The function is to provide stored energy and photosynthesize.
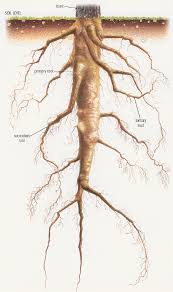
Roots systems
There are two types of root systems, the taproot system and the fibrous root system. Hemp has a taproot system, which means that it has one big root with smaller branches that spread out from the main root to absorb water and nutrients. When cutting a tap root in the width, you can see that the xylems are organized in the middle in the shape of an x/+ with the phloem organized around it. If you would look at a fibrous root, it would shaped in the form of a circle.
The xylem and phloem in the stem of hemp plants, are arranged in a circle near the outside of the stem. If you would take a look at the same place in a monocot plant, the vascular bundles would be scattered around.
Leaves
The Leafs have allready been spoke off, but there is more that distinguishes the monocot and dicot leaves than can be seen from outside. In hemp (dicot) leafs, there is a clear difference between the top and bottomside. The function of the top side (palisade) is to catch sunlight in order to initiate photosynthesis, while the bottom side is responsible for the exchange of water vapor and exchange of gasses, (where the stoma's are located). Above the palisade there is another layer, the dermal tissue, which protects the leaf. Between the palisade and the bottom side is the spongy tissue in which the vascular tissue is situated.
References:
Lecture 2 Plant Anatomy and Morphology2015_16.p, HAS Hogeschooldf, HAS
The Hemp (or cannabis) plant, is famous globally because of its iconic shape of leafs. In this post I'm going to talk more in dept about some characteristics of the hemp plant that are also recognisable from the outside, but may not be known for people who's knowledge does not go beyond the point of recognising the shape of the leaf.
Monocot or dipot?
The distinction between monocot and dicot plant is pretty easy to determine from outside. First of all, you can take a look at the flowers. If the flower is in parts of threes or a multiplied version of this, it is a monocot plant. If the flower is made up in parts of fours and fives of a multiplied version of this, the plan is a dicot.

(Source: http://www.ext.colostate.edu/mg/gardennotes/135.html)
Another way to indentify if a plant is a monocot or dicot, is to look at the leafs. Monocot leafs have the veins parallel to each other, while dicot leafs are branches and netlike. This is easy to see in the next picture, when comparing grass to a dicot leaf.

(Source: http://www.majordifferences.com/2014/04/difference-between-monocot-and-dicot.html#.Wb55c8hJbIU)
Is Hemp a monocot or dicot?
The leafs of the Hemp plant indicate that it is a dicot. But what other features can indicate whether hemp is a monocot or dicot? and what are the differences?
Cotyledons
This are the primary leafs in the seed of which the hemp plants has two (instead of one for monocots). The function is to provide stored energy and photosynthesize.

Roots systems
There are two types of root systems, the taproot system and the fibrous root system. Hemp has a taproot system, which means that it has one big root with smaller branches that spread out from the main root to absorb water and nutrients. When cutting a tap root in the width, you can see that the xylems are organized in the middle in the shape of an x/+ with the phloem organized around it. If you would look at a fibrous root, it would shaped in the form of a circle.
(Source: http://study.com/academy/
lesson/taproot-definition-examples.html)
StemThe xylem and phloem in the stem of hemp plants, are arranged in a circle near the outside of the stem. If you would take a look at the same place in a monocot plant, the vascular bundles would be scattered around.
Leaves
The Leafs have allready been spoke off, but there is more that distinguishes the monocot and dicot leaves than can be seen from outside. In hemp (dicot) leafs, there is a clear difference between the top and bottomside. The function of the top side (palisade) is to catch sunlight in order to initiate photosynthesis, while the bottom side is responsible for the exchange of water vapor and exchange of gasses, (where the stoma's are located). Above the palisade there is another layer, the dermal tissue, which protects the leaf. Between the palisade and the bottom side is the spongy tissue in which the vascular tissue is situated.
References:
Lecture 2 Plant Anatomy and Morphology2015_16.p, HAS Hogeschooldf, HAS

Comments
Post a Comment